Coalesce function returns the first non-null value
among the arguments.
Syntax:
Coalesce (expression [,..n])
Here is example using Coalesce function
Example
1
DECLARE @Str1 varchar(10),@str2 varchar(20),@Str3 varchar(20)
SET @Str2='Sql' , @Str3='Server'
SELECT COALESCE(@Str1,@str2,@Str3) As [Coalesce]
In above example @Str2 value is ‘Sql’ , @str3 value is ‘Server’ and @str1 values is Null because it not assigned any value .
Output:
It return’s “Sql” because Coalesce function return’s
first non null value.
Example
2:
Coalesce in select statement.
IF OBJECT_ID('Employee','U') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE Employee
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY ,
NAME VARCHAR(20),
SALARY INT
)
INSERT INTO Employee (NAME,SALARY) VALUES ('Rakesh',5000),(NULL,6000),('Naresh',7000) ,(NULL,8000)
SELECT * FROM Employee
In above Query Result ID 2, 4 of Name Column is null. We have
to replace Name Column null value to
some other value (“Madhu”) using
select statement.
SELECT ID,COALESCE(NAME,'Madhu') AS Name,SALARY FROM Employee
Output:
Example
3:
Coalesce in where condition.
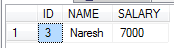
DECLARE @Lod_ID int =null
SET @Lod_ID =3
SELECT * FROM Employee where ID= COALESCE(@Lod_ID,ID)
Output:
It only select ID
value 3 row .because of in above @Lod_ID variable is set to 3 values . Coalesce funtion returns
first non-null value baecuse it’s
selects only 3 of ID colums rows only.
Example
4:
DECLARE @Lod_ID int =null
SELECT * FROM Employee where ID= COALESCE(@Lod_ID,ID)




Gud article
ReplyDelete